Slot Scanning Mammography
- Slot Scanning Mammography Center
- Slot Scanning Mammography Services
- Slot Scanning Mammography Software
- Slot Scanning Mammography Imaging

Slot Scanning Mammography Center
Slot scanning versus antiscatter grid in digital mammography: comparison of low-contrast performance using contrast-detail measurement
Early studies and clinical trials show that DBT is an improvement over full field digital mammography (FFDM) because it provides the radiologist with better image quality and more information.OBJECTIVE: This paper presents a simulation system to model the performance of a slot-scanning FFDM and DBT system.METHODS: A tissue-equivalent three. EOS® imaging system (also known as a slot-scanning device or slit-beam digital radiography system) is an x-ray technology that allows simultaneous acquisition of AP and lateral images of the entire body in a natural, erect position, and is also capable of performing three-dimensional reconstructions from these images.
The scope of this document is limited to FFDM systems 3 in the proposed new regulation 21 CFR 892.1715, product code MUE. 21 CFR 892.1715 – Full-Field Digital Mammography System. The FDA has approved the SenoScan slot-scanning Full-field Digital Mammography system. A high power Tungsten-target x- ray tube enables breast imaging with 0.22 s effective exposure time.
Slot Scanning Mammography Services
Abstract
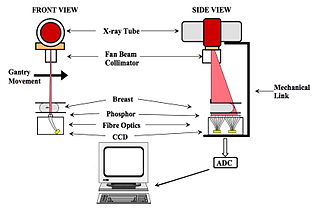
Slot scanning imaging techniques allow for effective scatter rejection without attenuating primary x-rays. The use of these techniques should generate better image quality for the same mean glandular dose (MGD) or a similar image quality for a lower MGD as compared to imaging techniques using an anti-scatter grid. In this study, we compared a slot scanning digital mammography system (SenoScan, Fisher Imaging Systems, Denver, CO) to a full-field digital mammography (FFDM) system used in conjunction with a 5:1 anti-scatter grid (SenoGraphe 2000D, General Electric Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI). Images of a contrast-detail phantom (University Hospital Nijmegen, The Netherlands) were reviewed to measure the contrast-detail curves for both systems. These curves were measured at 100%, 71%, 49% and 33% of the reference mean glandular dose (MGD), as determined by photo-timing, for the Fisher system and 100% for the GE system. Soft-copy reading was performed on review workstations provided by the manufacturers. The correct observation ratios (CORs) were also computed and used to compare the performance of the two systems. The results showed that, based on the contrast-detail curves, the performance of the Fisher images, acquired at 100% and 71% of the reference MGD, was comparable to the GE images at 100% of the reference MGD. The CORs for Fisher images were 0.463 and 0.444 at 100% and 71% of the reference MGD, respectively, compared to 0.453 for the GE images at 100% of the reference MGD.
Slot Scanning Mammography Software
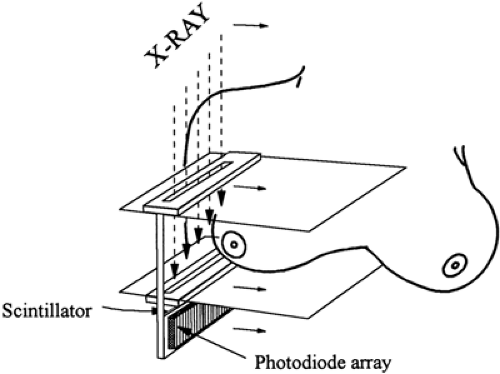
Slot Scanning Mammography Imaging
- Publication:
- Pub Date:
- May 2004
- DOI:
- 10.1117/12.535986
- Bibcode:
- 2004SPIE.5368..734L